Computers have become a necessity today. No matter what field, knowledge of computer fundamentals is very important. This article covers all the topics that you might need to know about computers.
So without any delay let’s dive into computer fundamentals. Beginning from the very basic and then slowly moving forward. Let us first check, what a computer is?
Content
What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic device that can perform various functions by taking input from the user, performing various processes on it with a set of defined instructions that produce an output.
The word computer is derived from the Latin word ‘computare’ which translates to ‘to compute’.
With the technology advancing each day computers are now not just limited to perform calculations or play videos. They have evolved and doing all those activities that humans can do that too faster and with zero errors.
We must know-how must have computers evolved over the years. Take a quick look at the different generations of the computer.
Advantages of Computers
- It helps in performing any task in the easiest and most efficient way.
- Helps us connect to the internet.
- Increases productivity by using fewer resources and time.
- Helps to organize a vast amount of data most efficiently and makes it quite accessible.
- The computer keeps you connected with all the information as well as your loved ones.
For details, check – advantages and disadvantages of Computers.
Generations of Computer
Over the centuries, mankind had invented various methods to make calculations easier and faster. But, Charles Babbage invented the first mechanical computer in the 1830s.
He invented the first digital programmable computer. Also known as the ‘Father of the computer’, he took the first step of what we today know as the computers. Since then, computers have been evolved on various levels. Till now we know 5 generations of computer.
1st Generation (1940-56)
Also called the vacuum tubes. These computers had vacuum tubes for the circuitry and used magnetic drums for storage. They used to take up a lot of space, consumed a huge amount of electricity, and relied on machine language (the most basic language understood by the computer).
2nd Generation (1956-63)
Replacing vacuum tubes with transistors, this generation’s computers were faster, smaller, cheaper, and consumed way less electricity. Despite many other problems like heating issues and circuit breakdown, these were a huge improvement. Instead of binary language, these computers used assembly language as input.
3rd Generation (1964-71)
These computers took a huge leap in the world of technology. Using integrated circuits instead of transistors, these were way more efficient, cheaper, and most importantly smaller. This was the first time keyboard and mouse were a mode of input.
4th Generation (1972-1980)
This was the era of VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration), integrating thousands of circuits in a small chip. Intel brought this revolutionary idea. They developed Intel 4004 chip. In 1981, IBM developed the first-ever computer for home use. Subsequently, Apple developed the Macintosh.
5th Generation (1980-present)
This is the era of artificial intelligence. The technology is still under development however, it has started showing its presence such as the voice recognition system. ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) has replaced VLSI in this generation of computers.
Basic Block Diagram of Computer
No matter which company the computer has been manufactured, the basic components of the computer and working remain the same. The computer consists 4 main units-
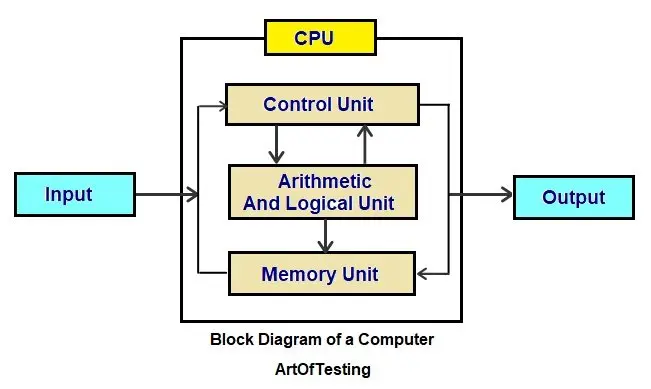
Input unit
All the data received by the computer goes through the input unit. The input unit comprises devices like a mouse, keyboard, scanner, etc. Each of these input devices of the computer acts as a mediator between the users and the computer.
CPU
Control Processing Unit or the CPU, is the brain of the computer. It works the same way a human brain works. The brain controls all the activities performed by humans.
Similarly, the CPU controls all the functions/tasks performed by the computer. The CPU further consists of two parts – ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) and CU (Control Unit).
Memory Unit
All the data that has to be either processed or has been processed is stored in the memory unit. The memory unit acts as a hub of all the data and transmits it to the required part of the computer whenever necessary.
Output Unit
All the information sent to the computer once processed is received by the user through the output unit. Output devices of computers like printers, monitors, projectors, etc. all come under the output unit.
The output unit displays the data either in the form of a soft copy like that in the monitor or the form of a hard copy, through a printer.
For details, check – block diagram of Computer.
Classification of Computers
Based on the type of data computers can process, the computers can be classified as digital, analog, and hybrid.
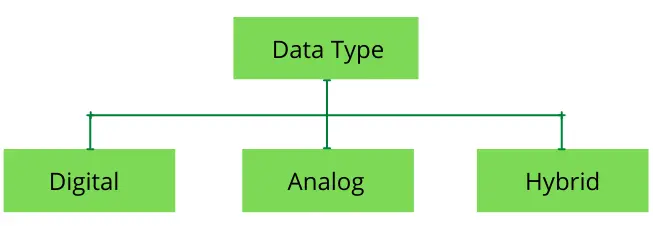
Digital
Our personal computers are an example of a digital computer. These computers accept input in the form of 0s and 1s, process, and provide the output.
Analog
These computers process analog data. An analog data keep varying and does not have any discrete value. They read the continuous change in the input, process it, and provide the output. Speedometer, thermometer are some of the examples.
Hybrid
Hybrid computers are a mix of both analog and digital computers. These computers perform a high level of calculations quickly and efficiently. It takes input in analog form, converts it into digital form, and then processes it to produce an output. Such computers are perfect for scientific purposes.
Based on the purpose, we can classify computers as microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframe, and supercomputers.

Microcomputer
Microcomputers also called personal computers are single-chip – bases systems. These are useful for personal use and can perform all the basic functions of the computer. These require very little space and are efficient too.
Minicomputer
Standing in between a microcomputer and a mainframe computer is the minicomputer. These computers are useful if people around 5 to 300 want to operate the system at the same time. You can see such computers at the billing counters of the malls or big institutions.
Mainframe
The mainframe computers come into use when a large number of people like in the health care or retail sector want to access data simultaneously. Mainframes thus are helpful for processing huge data.
Supercomputers
Supercomputers are the biggest and fastest computers. Such computers can process trillions of functions within a few seconds. These computers are specifically designed for scientific applications.
- Encryption decryption of passwords
- Weather forecasting
- Testing of nuclear weapons
- Scientific research of earth and other planetary systems, etc.
We know that the computer has two parts software unit and the hardware unit. But how does a interacts with the software system? Operating System is the perfect solution for such problems.
For details, check – Types of Computer.
Operating System
An operating system is an interface between the user and the software of the computer. The user gives commands through the hardware and the computer understands it, through the OS.
It is a link of computer hardware to the computer’s software and thus helping in perform functions in real-time. Some of the major examples of OS are – Microsoft, Mac OS, Linux.

Characteristics of the operating system
- Memory management – As the name suggests it is responsible for the management of the memory of the computer. The OS handles both, the primary and secondary memory. The OS performs the allocation and deallocation of memory for different processes in the computer.
- Device management -It also maintains the input/output traffic. Multiple inputs enter simultaneously. The OS decides which input needs to be processed first and which last. Accordingly, it assigns a particular process with the I/O device.
- Processor management – There are always multiple processes going inside the computer simultaneously. The OS prioritizes and schedules the processes. It also assigns the time required to perform each process. It maintains the real-time status of the process. If one process is complete it schedules the next process in the pipeline.
- File management – The computer stores all its files in a specific manner. The key function of the OS is to access these files in the fastest and the most efficient manner such that there is no delay in the execution of any program.
- Security – The OS is not only responsible for storing and managing data, but also securing it. The OS has a built-in module that prevents any unauthorized access to the private data of the user.
- Deadlock prevention – There are times when a single drive handles multiple processes. A deadlock situation occurs when a process enters into a waiting state. Meanwhile, the drive is held by another process. . Therefore, OS keeps a real-time check on all processes to prevent a deadlock situation.
These were the components of a single computer. But what happens when there are multiple users? How do multiple computers interact with one another? The concept of computer networking can explain this.
Computer Networking
When multiple computer systems are connected over through a communication channel to share information and resources it is called a computer network.
Computer networks can be classified based on requirements.
Classifications of computer network
- WAN – WAN or Wide Area Network is the connection of computers over a large geographical area such as a state, country, or even whole wide world. The WAN uses various types of communication channels like airwaves, telephone lines, or airwaves to interconnect different computer systems.
- LAN – LAN or the local area network is the connection of computers over a restricted area. Such as a school, university campus, an office building. Any geographical area within the radius of 10kms.
- MAN – MAN or the metropolitan area network connects computers over a large city or campus.
- PAN – PAN stands for personal area network. These devices connected belong to a single user. Such as pc connected to the printer, fax machine, video game console, etc. which can be connected both with wires and wirelessly.
Classification of Computer Network Based on Topology
The computer network can also be classified based on its topology. Topology is the spatial arrangement of computers. The arrangement is –
- Bus topology – The computers connected to a single communication line. Moreover, this one is less expensive to install as it contains only a single line.
- Star topology – The computers are connected to a single point or hub, and the arrangement looks like a star thus the name. this topology is the easiest to build and implement.
- Ring topology – A ring topology can be imagined as a bus topology in a closed loop. The first and last of computers are connected to form a ring. The resource is shared from one system to another with intermediate systems in between.
- Mesh topology – In this, each computer is connected creating a mesh or a net-like structure.
It should be kept in mind that no topology is better than the other. Each topology has its use and advantage and is used according to the requirement. All computer networks need to be connected globally. This can be made possible using the internet.
Internet
The internet is a global system where computer networks are connected and the world wide web. These computers are connected with either cable, telephone channels, or even wirelessly.
It is a medium to share resources from one point to another point. Secondly, is a physical infrastructure that connects all the computers and devices and does not belong to a single person.
It is a client-server based system where the laptops or our PCs act as the clients and they are connected to the internet through a local ISP(internet service provider). The server is the computer that holds all the websites and information. All the servers are stored at a place called the data centre.
But how are these clients and servers are identified in such a vast network? It is through the IP(internet protocol) address of the computer. The IP address is provided by the ISP of that computer. An IP is the address of each computer just like the addresses of our home to identify where are we located. An IP address is a string of numbers.
The server can find us using the IP address and similarly we can find the websites using their domain names. Domain names are also IP addresses. However, they are very long to remember thus easier way is to type the domain name such as Facebook.com, Youtube.com, Wikipedia, etc. The internet only understands IP address therefore, whenever you enter the domain name, the internet searches its IP address from a large directory -DNS (domain name server). It acts just like the phonebook directory. DNS contains all the numbers of the people.
Advantages of Internet
- It helps to connect people from all over the world by using social media, email, web applications, etc.
- The internet is now an online platform to buy different goods from all over the world.
- It is also helpful for operating online banking and thus making the whole process hassle-free.
- It is also a mode of entertainment. millions of videos, movies, and songs are available on the internet.
- With technologies like GPS (Global Positioning System), we can get instant directions to the specified destinations.
There some limitations of computers. But with all these advantages and features, the knowledge of computer fundamentals has become the need of the hour. The computers have helped us advance in several ways and will keep on doing so.